Is your website being labeled as fake or suspicious by internet users? This can potentially harm your online reputation and deter potential customers from visiting your site. The good news is that there's a simple solution to avoid this issue: domain forwarding.
By redirecting multiple domains to one main website, you not only boost the credibility of your business but also improve its overall SERP ranking. So how can domain forwarding benefit our businesses and how can we set it up?
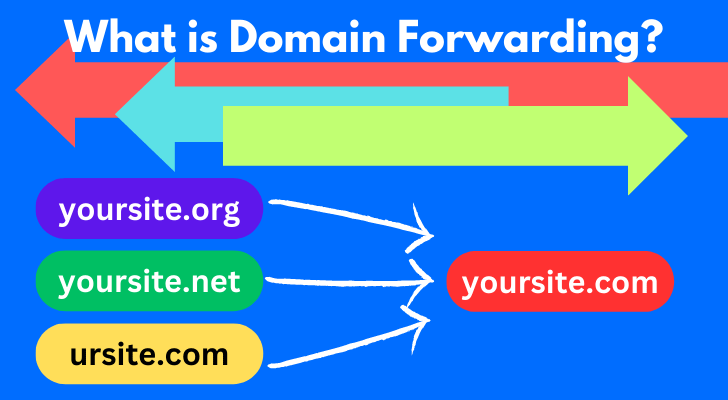
What is Domain Forwarding?
Domain forwarding is a process that redirects one or more domain names to a single domain. For example, if your company has various domain names such as .com, .net and .org, you can forward all of them to one main website. This means that when someone types in any of those domains, they will be redirected automatically to your primary website.
As you can imagine, it’s an effective solution for businesses with multiple domains because it not only saves time but also increases the visibility and credibility of their brand online. It also simplifies the management of these domains by allowing changes to be made from just one location.
Furthermore, domain forwarding can help protect your business from fraudsters who could potentially create fake websites using similar or identical domain names as yours. By owning multiple variations of your domain name and redirecting them all to your main site through forwarding, you are effectively safeguarding against such threats.
Domain forwarding is a powerful method that can benefit businesses in many ways including increased traffic and visibility on search engines while saving time on managing several domains separately.
How Domain Forwarding Can Benefit Your Business
Here are some of the key benefits:
Branding:
Domain forwarding allows you to register multiple domain names and forward them to your main website. This can help you to protect your brand and make it easier for customers to find you online.
Traffic:
If you have an older domain name with existing traffic, you can forward it to your new website to increase traffic and visibility. This can also help you to rank higher in search engines, as search engines take into account the age and popularity of a domain when ranking websites.
SEO:
Domain forwarding can also be used to improve your SEO efforts. By forwarding relevant domains to specific pages on your website, you can boost your rankings for specific keywords and phrases.
Expansion:
If you are expanding your business into new markets, you can use domain forwarding to target specific geographic areas. For example, if you are opening a new store in a specific city, you can register a domain name related to that city and forward it to your main website.
Simplicity:
Domain forwarding can make it easier for customers to find you online, by simplifying your web address. If you have a long or complicated domain name, you can register a shorter, easier-to-remember domain and forward it to your main website.
As you can see, domain forwarding itself might seem like a small feature, but it can have big benefits for your business. It can help you establish your online presence and protect their brand while improving their SEO efforts.
How To Set Up Domain Forwarding
Setting up domain forwarding is a simple process that can be done in just a few steps.
- Login to your domain registrar account where you have purchased the domain name.
- Navigate to the domain management section and look for the domain forwarding option.
- Choose the type of forwarding you want to set up. There are two types of forwarding options: 301 Permanent Redirect or 302 Temporary Redirect. (See below.)
- Enter the new domain name where you want to forward the traffic.
- Save the changes and check if the forwarding is working by typing the old domain name in the browser. If the forwarding is set up correctly, the browser should take you to the new domain name.
Note that it can take a few minutes (or longer) for the changes to propagate across the internet, so it may take a while before the forwarding becomes effective.
What’s The Difference Between 301 Redirects and 302 Redirects?
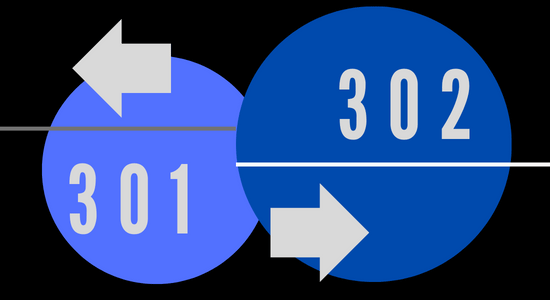
The main difference between 301 and 302 redirects lies in their purpose and how they are interpreted by search engines. 301 redirects are used for permanent URL changes, while 302 redirects are used for temporary URL changes.
301 Redirects
A 301 redirect is a permanent redirect, which tells search engines that the content has permanently moved to a new location. When a website visitor lands on a page that has been redirected with a 301 redirect, their browser is automatically redirected to the new page, and the search engines will update their index accordingly. 301 redirects are typically used when a page has moved to a new URL permanently, such as when a website undergoes a major redesign, or when the URL structure of a website changes.
302 Redirects
On the other hand, a 302 redirect is a temporary redirect, which tells search engines that the content has moved temporarily to a new location, and will soon be returned to its original URL. When a visitor lands on a page that has been redirected with a 302 redirect, their browser is automatically redirected to the new page, but search engines will continue to index the original URL, as it is assumed that the page will be returning to its original location. 302 redirects are typically used when a page needs to be moved temporarily, such as during website maintenance or when testing a new URL.
Tools For 301/302 Redirects
There are several tools you can use to implement a 301 or 302 redirect on your website, depending on your technical expertise and the platform you are using. Here are a few options:
Web hosting control panel:
Many web hosting providers offer a control panel that allows you to manage your website's files and settings, including redirects. You can typically find an option to add a redirect under the "Domains" or "Redirects" section of the control panel. Simply select the source URL you want to redirect, and choose the 301 or 302 redirect option.
Content Management System (CMS):
If you are using a CMS like WordPress, you can use a plugin like Redirection or Simple 301 Redirects to manage your redirects. These plugins allow you to easily set up redirects by entering the source URL and target URL and choosing the 301/302 redirect option.
.htaccess file:
If you have access to your website's .htaccess file, you can add a redirect code manually to implement a 301/302 redirect. The code will typically look something like this:
Redirect 301 /old-url/ http://www.example.com/new-url/
Redirect 302 /old-url/ http://www.example.com/new-url/
This code will redirect any visitors who land on the old URL to the new URL, using a 301 or 302 redirect.
Online redirect checker tools:
There are also a number of online redirect checker tools, such as Redirect Checker or Redirect Detective, that can help you verify your redirects and ensure that they are working properly.
Domain Forwarding and SEO
You can consolidate your online presence by redirecting one or more domains to your main website, which means you can avoid diluting your search engine rankings. So domain forwarding is a good method for website owners.
Another thing is, if you have recently changed your domain name or moved your website to a new URL, domain forwarding can help preserve the SEO equity that you have built up over time. You have your old URLs redirected to new ones with “301 redirects”, you will ensure that any inbound links pointing at the old site are redirected to the new site - this way link juice is being passed on and preserved.
On the other hand, you mustn’t abuse domain forwarding in an attempt to manipulate search engines. Google has taken measures against spammy practices such as creating multiple domains all pointing towards the same content - so make sure that any additional domains you forward are relevant and valuable sources of traffic themselves.
When used ethically and correctly, domain forwarding can be a good tactic in maintaining a strong online presence whilst preserving SEO equity.
Outdated Domain Forwarding Techniques
There are several outdated domain forwarding techniques that are no longer recommended because they can cause problems with search engines or user experience. Here are some examples:
- Meta refresh tags - This technique involves using a meta tag in the HTML of a website to automatically redirect visitors to another page after a specified time delay. This technique is no longer recommended because search engines may consider it a sneaky or spammy tactic.
- JavaScript redirects - This technique involves using JavaScript code to redirect visitors to another page. Like meta refresh tags, this technique can be considered spammy or sneaky by search engines and may cause problems with user experience.
- Frame forwarding - This technique involves creating a page with a frame that displays the content of another page, effectively forwarding visitors to the other page. This technique is no longer recommended because it can cause issues with search engines, as the content on the original page may not be indexed.
Instead of these outdated techniques, it is recommended to use 301 permanent redirects for domain forwarding, as this is a widely accepted and search engine-friendly method.
Temporary Domain Forwarding
I’ve talked about the main purpose of domain forwarding, which is usually permanent forwarding. The option is good for businesses that have rebranded or changed their name and want all traffic directed to their new website.
Whereas temporary forwarding, also known as URL masking, allows the original domain to be displayed in the browser while still directing users to a different website. It's useful for marketing campaigns where you want a specific URL displayed but direct users elsewhere.
Link Shortening Services
Link shortening services such as bit.ly and Pretty Links are a form of domain forwarding. When you use a link shortener, you are essentially creating a shortened URL that redirects to the longer URL of the original page.
For example, if you use a link shortener to create a short URL for the page "https://www.example.com/long-url-page.html," the short URL might look like "https://bit.ly/xXxxY".
When a user clicks on the short URL, they are redirected to the original page URL.
Link shorteners can be useful in a number of contexts, such as social media marketing or email campaigns, where you want to share a long URL in a way that is easier to remember or more visually appealing. They can also provide additional tracking and analytics capabilities, allowing you to monitor the performance of your links and gain insights into your audience.
Note that some link shorteners may be perceived as spammy or untrustworthy by users, particularly if the link destination is not clearly visible or if the URL is unfamiliar. Therefore, you really should use link shorteners judiciously and transparently, and ensure that users can trust the links you share.

How Many Domains Should You Forward?
If your brand/brand name is unique and distinctive, you may not need to buy similar domain names, as there is little risk of confusion with other businesses or brands. But if your brand name is common or generic, you may want to consider buying similar domain names to prevent competitors or cybersquatters from using them to mislead or confuse your customers.
For example, Amazon also owns other similar domain names such as amozon.com, anazon.com, etc. and uses domain forwarding. So if a user mistypes it “amozon” or “anazon” instead of "amazon", they’ll still be directed to amazon.com.
When buying similar domain names, consider the following factors:
- Variations of your business or brand name - You may want to buy domain names that include common misspellings or variations of your business or brand name to prevent confusion with your customers.
- Geographic variations - If your business operates in multiple geographic regions, you may want to buy domain names that include the names of those regions to make it easier for customers in those regions to find your website.
- Keyword variations - If your business is focused on a specific product or service, you may want to buy domain names that include relevant keywords to improve your search engine visibility and attract more traffic to your website.
Ultimately, the number of domain names you can buy will be based on your budget, while taking into account the potential benefits and risks associated with each domain name. It is important to choose domain names that are relevant, easy to remember, and not confusing to your customers.
What Is Domain Forwarding? Final Words
Domain forwarding is a useful practice that allows website owners to redirect traffic from one domain to another. Whether you're changing your domain name, consolidating multiple domains, or redirecting visitors to a new page, domain forwarding can help you maintain your search engine rankings, preserve your brand identity, and improve the user experience for your visitors.
Implementing domain forwarding should be part of your branding strategy to ensure your online presence remains consistent across all platforms. So don't let fake domains ruin your reputation, use the power of domain forwarding.